Jessica Ennis-Hill was a track athlete who specialized in heptathlon. Her professional sports career started in 2005 and she retired in 2016. That was 11 years of athletic competition that brought Jessica Ennis-Hill fame as a popular British athlete. Now she shares her knowledge of fitness and athletic training with the general public. Jennis.com provides information for women related to nutrition and exercise. One subject Jessica Ennis-Hill discusses is the need for women to do weight training. While she discusses benefits, Ennis-Hill tries to put to rest concerns or fears of women “bulking out.” Terms such as bulk and tone are general descriptions of muscle mass. The words are discussing the amount of muscle mass, rather that an exercise science concept. Normally the phrase is bulk up not “bulk out.” Jessica Ennis-Hill insists ” the majority of women are more likely to become lean, strong and powerful if they add weight and resistance to their workouts, rather than bulky.” Depending on genetics, exercise frequency, and anthropometric measurements women bodies can vary in response to weight training. Some women could gain more muscle than others. Jessica Ennis-Hill asserts that their is a “‘right” type of weight training. Training is adjusted depending on what the fitness goal is. If exercise and athletic training are done consistently it will produce results. Women can gain muscle and it should not be seen as undesirable.
The terms lean and toned are gender coded words. When doing toning, it just becomes a women’s connotation for building muscle. Lean just means limited body fat. Women can have different degrees of muscularity. Aesthetics differ from training for athletic performance. Jessica Ennis-Hill mentions the physique aesthetics. Doing sports can develop muscle. The legs of a track athlete are muscular from running. Bodybuilders train all muscle groups, for aesthetic purposes.
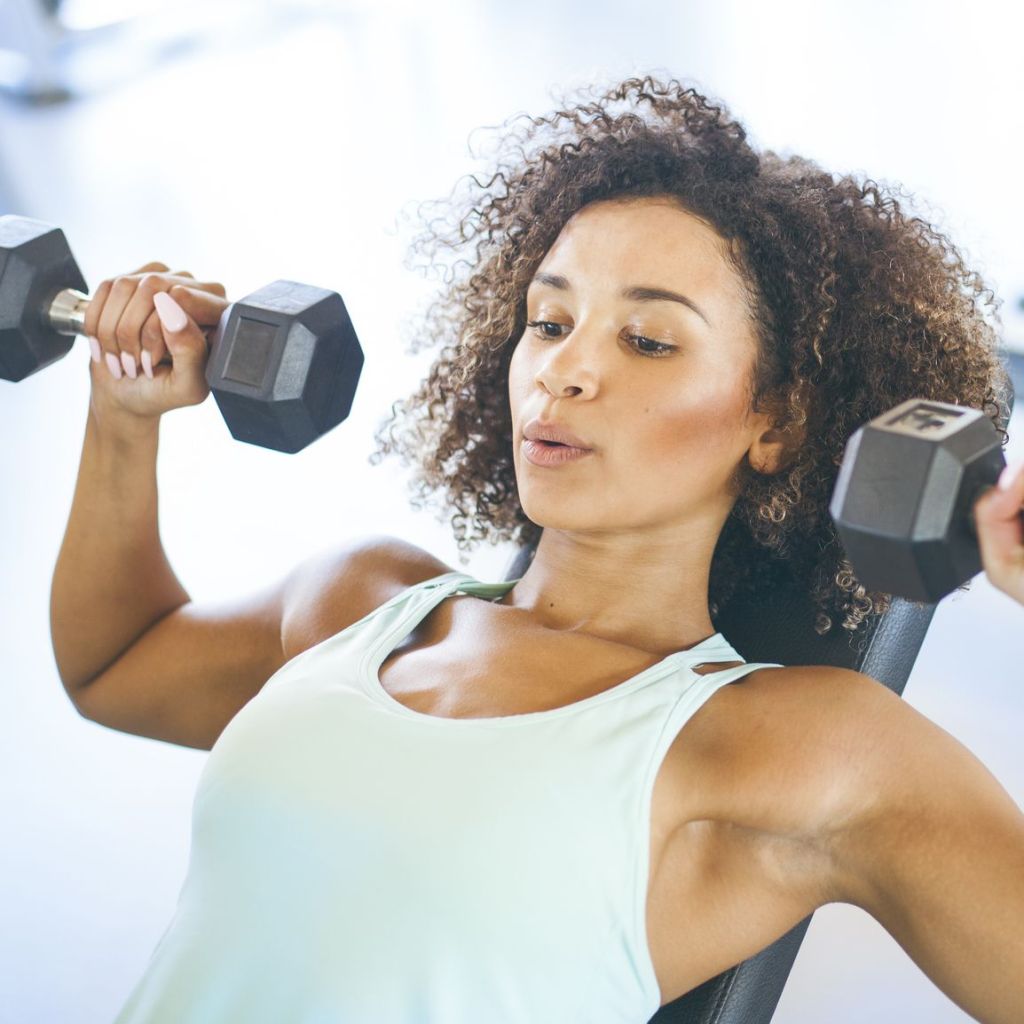

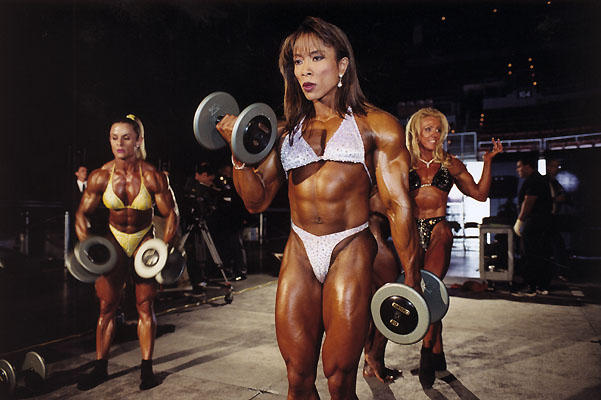
Weight training has multiple applications. It can be used for improve sports performance. Lifting can be a method of health maintenance. Depending on various factors women’s bodies can look different as the result of exercise stimuli.
Certain women might not obtain the same physique. Body type prior to training plays a role. Women with a more mesomorphic body type will have higher amounts of muscle mass from training. Thinner women are going to struggle to gain weight. Women who exercise for general health maintenance might not appear toned. Gaining an amount of muscle requires consistent diet and exercise.
Women are concerned about gaining a female bodybuilder physique. Jessica Ennis-Hill explains this is difficult due to women’s endocrine physiology. Even if it was easy, the female bodybuilder physique should not be deemed unpleasant. The best bodybuilders are women who have won the Ms. Olympia multiple times. Estrogen enables women to produce more fat. Women still have the same muscle fibers. Mass and size differ among the sexes. Women bodybuilders consume higher amounts of protein and train at a higher intensity. Jessica Ennis-Hill calls their physiques “bodybuilder big.” Even among bodybuilding there are multiple classes. Bikini, figure, fitness, physique, and open bodybuilding have different levels of muscularity. Bikini and figure are closest to what Ennis-Hill would label as toned.
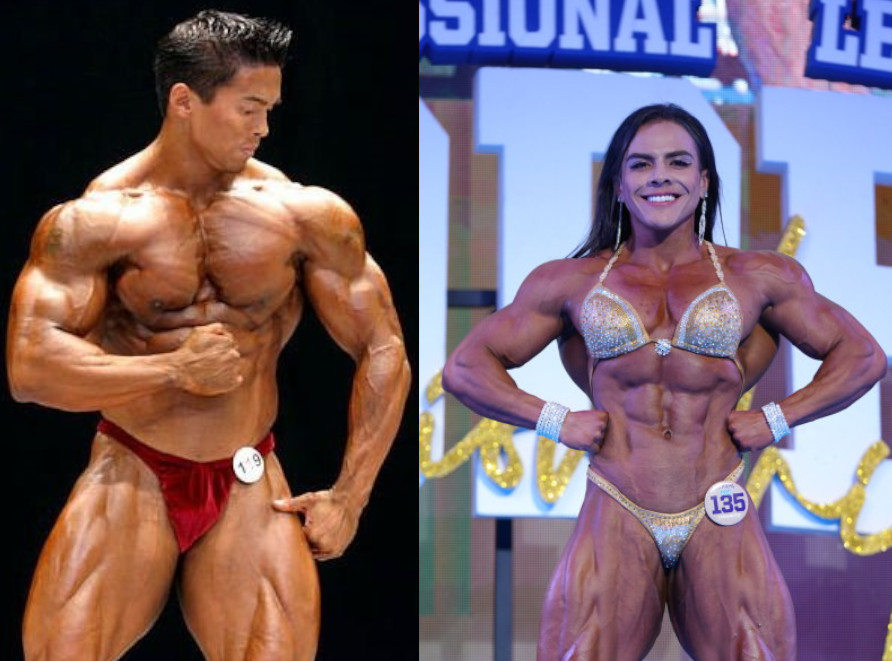



Women tend to resist doing weight training for fear of getting a massive physique. Estrogens allow women to carry a certain amount of fat, no matter what somatotype. The muscle fibers of males are bigger and total mass is bigger as well. Women bodybuilders weigh less than the average American man.
The concerns about muscle should be discarded. The large female bodybuilders based on weight are not some hulking mass. Women compete at weight ranges between 115 to 170 lbs. The women that compete do not have “Arnie style bulk.” Men on stage can weight more than 200 lbs. Compare male and female bodybuilders they do not look the same. Women scared about getting a body similar to a man is baseless. Bodybuilders have to be very diligent to create a physique. Athletic training sessions could be two hours a day. Body parts are exercised on specific days. Cardiovascular exercise is not a requirement as Jessica Ennis-Hill suggests. Leg presses can build the lower body just as much as running. A high protein diet combined with vegetables, nuts, and seeds add to muscular hypertrophy. According to the NHS women require 45 grams of protein daily. Women bodybuilders need more to maintain muscle mass. Jessica Ennis-Hill estimates that a woman’s caloric intake needs to be 15% higher. The terms bulking phase refers to gaining muscle mass. The cutting phase involved losing fat and developing definition. Ennis-Hill then states that caloric intake is reduced to 15% for getting definition. Bodybuilding is a complex production that involves nutrition, exercise science, and myology.
Weight training has numerous benefits to health. Keeping a healthy body weight is essential. Obesity and getting overweight can be related to certain factors. Lack of exercise and high caloric intake can result in excess body weight. Sugar and saturated fat being part of a daily diet can overtime be deleterious to health. Jessica Ennis-Hill explains that weight training can be a method of fat loss. Adding muscle requires more energy to maintain. It burns more calories in relation to fat tissue. This means resting metabolic rate will be higher.
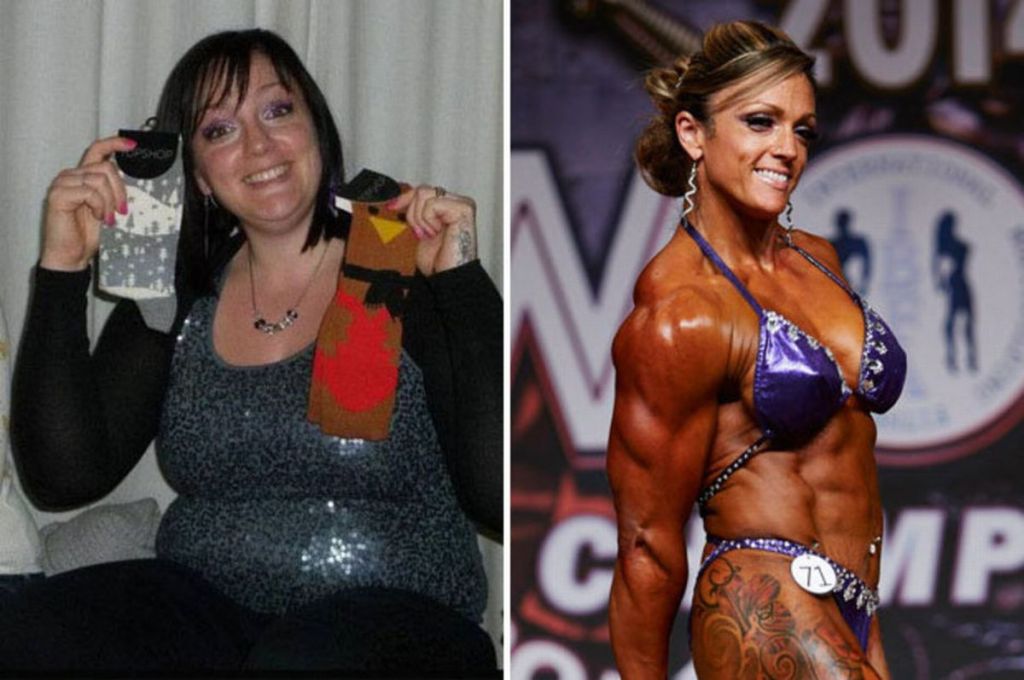

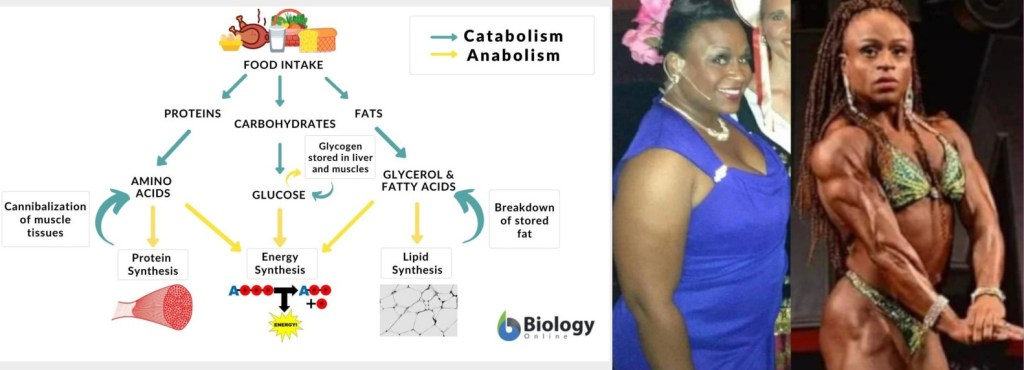
Women have turned to weights as a means of fat loss. Some athletes who compete began their fitness journey overweight. Jessica Ennis-Hill cites a 2014 study in which showed the correlation between weight training and higher resting metabolic rate. Over the span of 9 months resting metabolic rate increased by 5%. More research would be required to see how this could be made more effective. What has been confirmed is that weight training can be used for losing body fat.
The health of the skeletal system can be protected through weight training. As people age, bone mass and density decrease. When a person lifts weights it builds bone mass. The skeleton is the support for the muscle of the human body. Getting enough calcium and vitamin D is essential. Exercise should also be included with a program of maintaining bone. Osteoporosis describes a disease in which the bones become more porous. When this occurs bones are subject to break easily. Women are at higher risk considering that their bone density is lower. Bone has to continually rebuild. Osteoblasts have to work to replace lost bone.

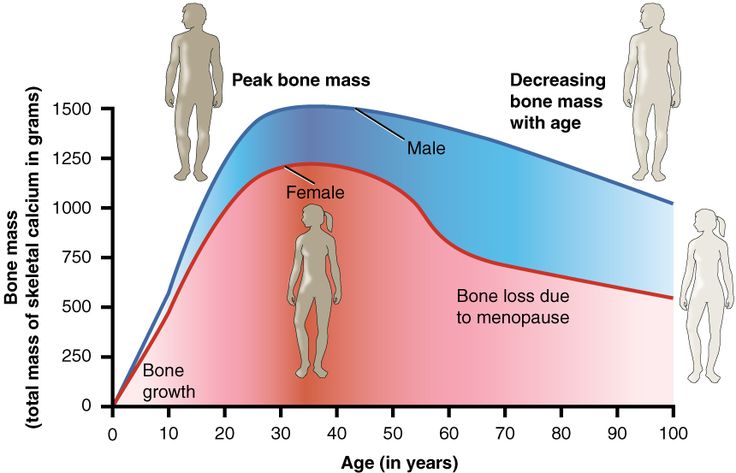

Bone mass changes through the aging process. Children are still growing, which explains their lower bone mass. Elders are losing bone mass.
When doing weight training bone cells are assisted in replacing lost bone. Bone mass is at its peak by age 30, but declines gradually with age. Menopause can be a factor in bone loss. Race can be a factor besides age and sex. Those of European and Asian descent can be at higher risk for osteoporosis. Women should build as much musculoskeletal mass as possible to prevent bone diseases.
Jessica Ennis-Hill was a track athlete, so running is mentioned. Women who start weightlifting might not be trying to run faster. Running can be a method of preserving musculoskeletal mass. A person does not even need to run to do this. Walking can also be beneficial. The problem is being sedentary for extended periods of time. This does not only effect bone, but the circulatory system. Jessica Ennis-Hill should clarify the difference between sprinting and marathon running. Strength is more important to sprinting. A runner requires enough type II muscle fibers to propel them. The marathon runner needs more endurance and type I muscle fiber. When Jessica Ennis-Hill competed her weight training was most for upper body strength. That is needed for javelin and shot put events.




Lower body strength development required polymetric drills. Doing this allowed Jessica Ennis-Hill to improve her performance. Her athletic training differs beyond just lifting weights. Running really is not required as part of strength training program. While this topic may seem as a non-sequitur, another application can be noted. When doing an exercise program it can become monotonous . A person can lose interest or quit. Adding another type of exercise can prevent boredom with physical activity.
Jessica Ennis-Hill refers to a weight training style. A better description is training method. There are options available. A novice and either chose to lift lighter or a larger amount. Lifting smaller weights with many repetitions can increase muscular endurance. Lifting heavier weights with lower amount of repetitions can increase strength. Both can build strength. Lifting lighter with more repetitions can still produce strength gain. Liftin heavier just could make it faster. Progressive overload is the preferred training method for maximum strength gains. A novice should start with a low amount of weight. They should increase it when they no longer struggle to lift a certain amount. To prevent injury always have proper form and do not lift more than you can handle. Method describes a specific approach. Jessica Ennis-Hill calling it a weight training style is more of a misnomer.
Jessica Ennis-Hill also proposes some general recommendations. Getting enough sleep and recovery is required for muscular hypertrophy. The reason relates to the production of insulin -like growth factor-1. This hormone aides in muscle repair from exercise. Protein consumption needs to happen a certain times a day. Meals times should be consistent and structured around workouts. Eating protein before a workout can give a person more energy. Food acts as fuel for the body the same way gasoline runs a car. Eating afterwards contributes to muscle growth. Jessica Ennis-Hill makes the suggestion of drinking milk or eating yogurt as a protein source. That selection is not ideal for someone who is lactose intolerant. Protein can be found in eggs, fish, chicken, and quinoa. These can be substitutes. These are basic guidelines that should be committed to memory.
Jessica Ennis-Hill concludes with expressing “rather than making you bodybuilder big, the right strength training sessions will actually help you feel great, rev up your metabolism and help with toning and strength gains.” Toning is building muscle and there is nothing wrong with women having developed muscle. Many women bodybuilders also feel great from training and notice an improved metabolism. Strength gains can also be a product of competing in bodybuilding competitions. Women should not reject building muscle no matter how much. Jessica Ennis-Hill’s physique could probably win a figure or physique class competition. At onetime, she was concerned about her muscular body. Jessica Ennis-Hill then relinquished body image pressure and embraced weight training. Someday, the women’s bodybuilding physique will not have negative connotations attached to it. Women now are at least opening up to weight training, but do not embrace muscularity. Jessica Ennis-Hill gives a lucid explanation about why weight training is a great investment for women’s health.



